Sony and Apollo Global Management are currently in talks about teaming up to place a bid for Paramount Global (NASDAQ: PARA). This discussion points towards a joint venture aimed at potentially taking Paramount private. On its own, Apollo has already made a significant play, putting forth an $11 billion offer for Paramount’s film and TV divisions. Then a $26 billion offer to buy the company outright. This aggressive move has resulted in a noticeable uptick in Paramount’s stock prices, underscoring strong market interest and the financial allure of such a deal. Apollo’s proven prowess in managing media and entertainment assets lends substantial weight and appeal to their proposal.
Meanwhile, Skydance Media is setting the stage for a possible merger with Paramount, following the latter’s decision to turn down Apollo’s $26 billion bid for a full acquisition. Paramount seems to prefer a merger that better suits its current projects and strategic goals, including the enhancement of its streaming platform, Paramount+. This preference is likely influenced by Skydance’s history of successful collaborations with Paramount, such as the blockbuster hit “Top Gun: Maverick,” suggesting that a merger could seamlessly integrate their respective studio operations.
The Paramount Global board gave the nod to Skydance Media on Wednesday, allowing for a 30-day exclusivity period for negotiations, Reuters reported. LightShed Ventures’ Rich Greenfield in an interview with CNBC, said he’s surprised Paramount turned down Apollo’s alleged $26B all-cash bid, instead opting for a Skydance deal.
For Paramount shareholders, these developments present two distinct paths:
Apollo’s Proposal: This bid not only injects a substantial cash reserve into Paramount but also offers the potential for high returns, drawing on Apollo’s history of revitalizing underperforming assets. Shareholders seeking immediate financial uplift might find this option particularly attractive.
Merger with Skydance: This route promises a more strategically coherent partnership. Merging with Skydance could yield long-term advantages by merging content creation and distribution efforts. This might appeal more to shareholders focused on sustainable growth and operational synergy.
Shareholders’ choice between these two will likely depend on their investment timeline and risk appetite. While Apollo’s offer is tantalizing in the short-term with its premium market value, a partnership with Skydance might pave the way for more profound strategic growth, potentially enhancing long-term value, especially with the expansion of Paramount+ in the competitive streaming market.
Regarding the financial details of both propositions:
Apollo’s Bid: Initially at $11 billion for Paramount’s key divisions, Apollo’s offer later surged to $26 billion for the whole company, a figure well above the company’s stock price of $12.51 at the time. This latter offer represented a more significant premium, though the exact per-share premium was not detailed, however we can try to quantify that using the formula below.
To calculate the share price for Paramount Global (NASDAQ: PARA) with a market capitalization of $26 billion and 652 million shares outstanding, you would use the following formula:

Plugging in the numbers minus the approximate $16.1 billion last reported Paramount debt and add the $2.46 billion in cash on hand:

Therefore, the buyout would have come in at around $20.95/share from Apollo and Sony.
These are just estimated numbers based on recent filings and are subject to change.
Merger with Skydance: The specifics of the financial terms with Skydance have not been made public. Instead, the focus has remained on the strategic and operational benefits of the merger, rather than the direct financial metrics.
For shareholders evaluating these options, the immediate financial benefits of Apollo’s offer are clear, particularly given the premium on the current stock price. In contrast, the Skydance merger presents a strategic vision, with potential financial benefits articulated more in terms of long-term value creation.
In summary, while Apollo’s bid presents a clear immediate financial benefit, the merger with Skydance offers broader strategic advantages, providing a potentially more balanced approach for shareholders seeking both immediate returns and future growth opportunities. It’s possible that Paramount circles back to reevaluate the Appolo bid or receives an offer from the proposed combined bid from Sony and Apollo.
About Skydance and the Potential Merger Deal:
Skydance Media is led by David Ellison. This potential merger is significant in the media industry, reflecting the strategic moves by companies to adapt to changing media consumption patterns and industry consolidation pressures.
Skydance expects to make just over $1 billion in revenue in 2024 with Ebitda of $90 million, and in 2025 expects $2.29 billion in revenue and $322 million in Ebitda, the report added, citing people familiar with the matter. (Reuters)
I will be paying close attention to additional merger details as they are released.
Paramounts Current Share Statistics and Financial Metrics
As of April 2024, Paramount Global (PARA) has approximately 652 million shares outstanding (YCharts) (CompaniesMarketCap). The company’s market capitalization is currently about $9.17 billion, reflecting a range of valuations over the recent fiscal quarters (Yahoo Finance).
Ownership of Paramount is predominantly institutional, with 68.86% of the shares held by institutions and 16.23% by insiders (Yahoo Finance). The major institutional shareholders include Berkshire Hathaway, which holds 10.35% of the shares, Vanguard Group with 9.53%, and BlackRock with 7.14% (Yahoo Finance).
Paramount’s enterprise value stands at approximately $22.57 billion as of the end of 2023 (Yahoo Finance). The company operates with a trailing price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio of 21.66 and a forward P/E ratio projecting at around 9.85 (Yahoo Finance). This provides an insight into the valuation metrics and how the market is pricing the company’s earnings growth potential relative to its current profit generation.
For Paramount Global, the range of valuations mentioned previously includes several financial metrics as of December 31, 2023. Here are the specific valuation figures:
Market Capitalization: Ranged from $8.52 billion up to $14.67 billion throughout the fiscal year (Yahoo Finance).
Enterprise Value: Varied from $22.57 billion to $29.06 billion over different quarters (Yahoo Finance).
Price-to-Earnings (Trailing): Was recorded at 21.66 at the end of the last fiscal year (Yahoo Finance).
Forward Price-to-Earnings: Fluctuated, with estimates like 9.85 and as high as 22.08 in earlier quarters (Yahoo Finance).
These figures provide insights into how the market values Paramount based on its current and future earnings, as well as the overall enterprise value relative to its revenue and EBITDA.
Paramount Recently Declared a Cash Dividend
Paramount Global (NASDAQ: PARA, PARAA) announced that its Board of Directors has declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.05 per share on both its Class A and Class B Common Stock. The dividend will be payable on July 1, 2024, to stockholders of record at the close of business on June 17, 2024.
Short Interest (SI) 15.6% and the Top 13 Major Holders
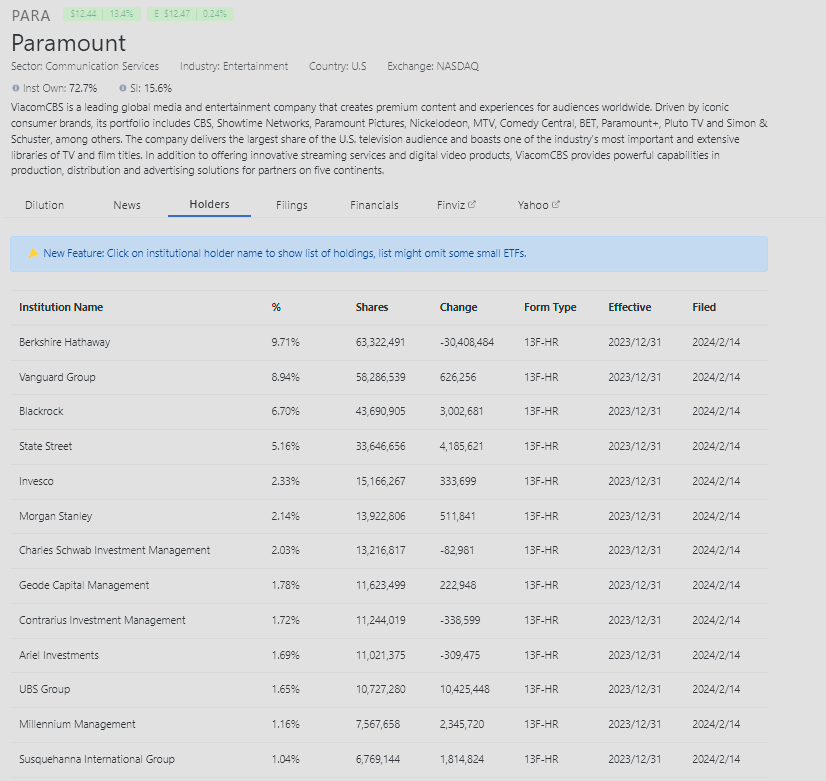
Source: DilutionTracker
Paramount’s Income Statement and Balance Sheet
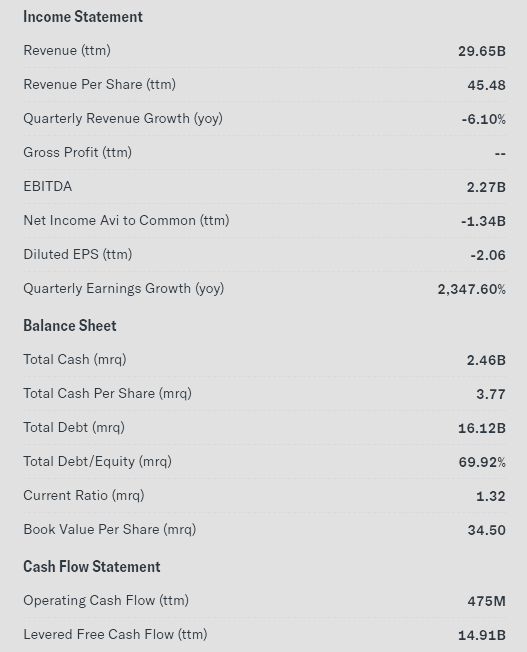
Source: Yahoo Finance
For more information on Paramount Global
Investor Presentation February 2024
Risk Factors: Strategic Considerations and Financial Implications
In evaluating the potential acquisition of Paramount Global by Sony and Apollo Global Management, and the possible merger with Skydance Media, shareholders and stakeholders should consider the following risk factors:
1. Market Dynamics and Competitive Pressure
Volatility in Media Sector: The media industry is notoriously volatile with rapid changes in consumer preferences and technological advancements. A major acquisition or merger during such unstable times could lead to unforeseen challenges.
Increased Competition: Merging with or acquiring a major player like Paramount could provoke competitive responses from other industry giants, potentially leading to a price war or increased spending on content acquisition.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Risks
Antitrust Scrutiny: Any significant merger or acquisition in the media sector is likely to attract close scrutiny from regulatory bodies, which could delay or even prevent the completion of the deal.
Compliance Costs: Meeting regulatory approval might involve commitments or concessions that could be costly and affect the profitability or strategic value of the deal.
3. Integration Challenges
Cultural Fit: Integrating two large entities like Paramount and Skydance, or incorporating Paramount into Apollo’s existing operations, may encounter cultural and operational misalignments which could impede strategic synergy and operational efficiency.
Management Alignment: Differences in management philosophy and business operations could lead to conflicts, potentially stifling decision-making processes and innovation.
4. Financial Exposure
Debt Levels: Financing a buyout or merger often involves taking on significant debt. The increased leverage could strain financials, especially if the anticipated synergies do not materialize as expected.
Impact on Share Value: While Apollo’s bid might inflate Paramount’s stock price temporarily, there is a risk of decline if the acquisition does not lead to improved performance or if the market conditions change adversely.
5. Strategic Risks
Opportunity Costs: Engaging in a merger or acquisition might divert resources and focus from other strategic opportunities, possibly resulting in missed chances to innovate or expand in other areas.
Long-Term Viability: The attractiveness of immediate financial gain from Apollo’s proposal needs to be weighed against the long-term strategic benefits of a merger with Skydance, which might offer more sustainable growth but with delayed financial benefits.
6. Market Reaction
Investor Confidence: The reaction of investors to the merger or acquisition news could affect stock prices. Negative perceptions or skepticism about the deal’s benefits could lead to stock volatility.
Stakeholder Acceptance: Employees, customers, and other stakeholders’ acceptance of the merger or acquisition is crucial for smooth transition and operation. Resistance from these groups could hinder progress and damage the brand.
7. External Factors
Economic Conditions: Economic downturns or financial market instability could impact the feasibility or desirability of the deal, affecting everything from financing terms to strategic priorities.
Geopolitical Issues: International regulatory environments, political unrest, or changes in trade policies, especially relevant for global entities like Sony, could complicate or undermine the deal.
By carefully assessing these risks, stakeholders can make more informed decisions regarding the proposed transactions involving Paramount Global. It’s essential to balance the potential for immediate financial uplift against the broader strategic alignment and long-term growth prospects that these corporate movements might bring.
by Steve Macalbry
Senior Editor,
BestGrowthStocks.Com
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered financial or investment advice. We do not hold any form of equity in the securities mentioned in this article. Always consult with a certified financial professional before making any financial decisions. Growth stocks carry a high degree of risk, and you could lose your entire investment.